Stack
[[toc]]
Abstract
todo
Stack Problem
Valid Parentheses(括号匹配)
堆栈在处理递归问题时非常有用,对于括号匹配,是栈应用的经典案例:
-
Initialize a stack S: 初始化栈
-
Process each bracket(括号) of the expression one at a time.
-
If we encounter an opening bracket, then we check the element on the top of the stack. (遇到左括号则入栈)
-
If the element at the top of the stack is an openning bracket of the same type, the we pop it off the stack and continue processing. (栈顶元素和外面相匹配,则出栈继续)
-
Else this implies an invaild expression.
-
In the end, if we are left with a stack still having elements, then this implies an invaild expression. (栈不空则表达式非法)
Implementation:
简单版本:
def isValid(self, s: str) -> bool:
stack = []
for ch in s:
if ch in ['(', '[', '{']:
stack.append(ch)
else:
# for the case "]"
if stack == []:
return False
if ch == ')' and stack[-1] != '(':
return False
if ch == ']' and stack[-1] != '[':
return False
if ch == '}' and stack[-1] != '{':
return False
stack.pop()
return stack == []优化版本,基本思路一致:
def isValid(self, s: str) -> bool:
stack = []
mapping = {"]":"[", "}":"{", ")":"("}
for ch in s:
if ch in mapping.keys(): # 右括号,进行判断
if stack == []:
return False
if stack.pop() != mapping[ch]:
return False
else:
stack.append(ch) # 左括号,入栈
return stack == []Explaination:
- 我们遍历字符串 s, 遇到左括号则入栈,遇到右括号 (keys) 则弹出栈顶元素进行比较(在栈非空的前提下)
- 最终返回值:栈空则合法,等价于
return stack==[]
Validate Stack Sequence
给定入栈和出栈序列,判断是否合法:
def validateStackSequences(pushed: 'List[int]', popped: 'List[int]') -> bool:
i = 0
stack = []
for x in pushed:
stack.append(x)
while stack and i < len(popped) and stack[-1] == popped[i]:
stack.pop()
i += 1
return stack == []
# returen i == len(poped)注意到我们不改变 pushed 和 poped, 而是使用一个 stack = [] 作为辅助操作。
当没有找到与 stack 栈顶元素相等的元素时,不停地往 stack 中添加元素,
Next Greater Element
https://leetcode.com/problems/next-greater-element-i/
这道题目的大意是给定两个 List, 比如:
find_nums: [4, 1, 2], nums: [1, 3, 4, 2]
需要找出 nums 中 find_nums 对应的下一个比它大的元素,未找到就返回 -1, 在这个例子中的结果是:
res: [-1, 3, -1]
def nextGreaterElement(find_nums, nums):
# [4, 1, 2]
# [1, 3, 4, 2]
# [-1, 3, -1]
stack = []
dic = {}
for num in nums:
while stack != [] and stack[-1] < num:
dic[stack[-1]] = num
stack.pop()
stack.append(num)
res = []
for find_num in find_nums:
res.append(dic.get(find_num, -1))
return res当栈顶元素小于 num 时,在字典中添加栈顶元素, num 表示栈顶元素的 next greater element 是 num
stack 在上述例子中的顺序变化为:[1] -> [3] -> [4] -> [4, 2]
dic 为 {1: 3, 3: 4}
用两个栈实现一个队列
这是面试中的经典问题,应当熟练掌握。
所谓两个栈实现一个队列,应当是指实现队列的 尾插 和 头删 两个操作。
我们定义两个栈 S1 和 S2:
- S1:只进行插入数据
- S2:删除 S1 中的数据
!注意 S2 不为空时不要从 S1 中添加数据,类似于下图三的情况。
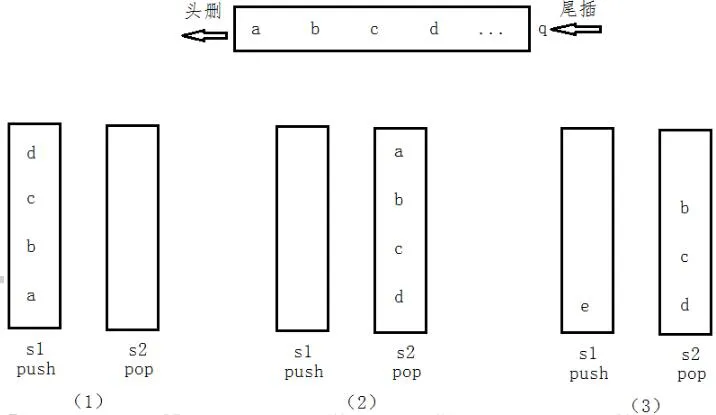
代码实现如下,思路就是使用两个栈,一个做插入,一个做删除:
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.s1 = []
self.s2 = []
def push(self, node):
self.s1.append(node)
def pop(self):
if self.s2 == []:
while self.s1:
self.s2.append(self.s1.pop())
return self.s2.pop()
return self.s2.pop()用两个队列实现一个栈
括号匹配
后缀表达式
修改历史11 次提交
- chore: reorganize image assets and add sharp dependencyxiaocheng··
7661b66 - refactor: reorganize documentation structure and update Navbar componentxiaocheng··
2fb8f42 - chore(project): clean up obsolete configuration and build artifactsxiaocheng··
3574bd3 - new struct for lblogsxiaocheng··
8c9b28e - move blogs to docsxiaocheng··
c8535a0 - update codechenweigao··
e4c6887 - update fix: timeline errorchenweigao··
fb4b591 - update some imageschenweigao··
e014780 - update Datechenweigao··
3c14689 - init v3chenweigao··
b770fc2 - init v2chenweigao··
505f81b